Neurofeedback Therapy and Training that your Brain Needs
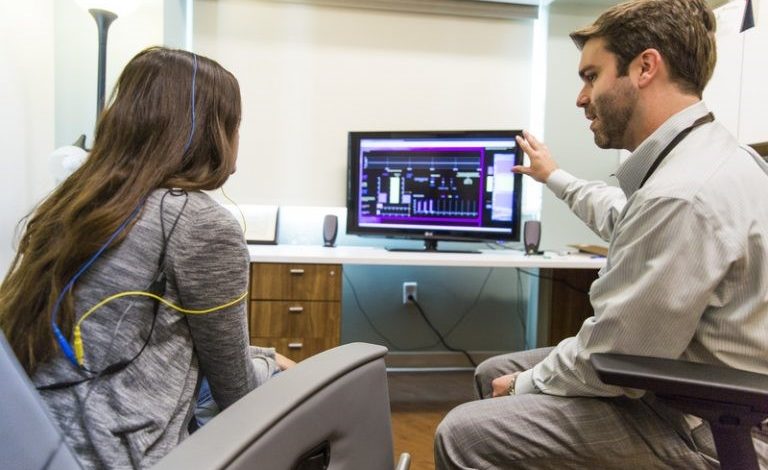
Neurofeedback Therapy: Everything one does throughout the meeting is determined by the problem one attempts to solve. One might, for instance, view it on display, calm one’s mind and join music, or that enjoy a computer game. One may be sitting prone or seated on a seat.
Neurofeedback Therapy:
The notion of neurofeedback therapy is indeed not novel. For hundreds of years, it has been the topic of investigation. Neurofeedback is a technique that allows people to influence their brain oscillations intentionally. During neurofeedback therapy, electroencephalography collects. Then, utilizing an endless vicious circle, its aspects are retrieved and supplied to participants in the shape of sound, visual, or a mix of the two. As a result, electrophysiological elements illustrate independently. Throughout this method, the individual develops awareness of the modifications that happen throughout the exercise and is capable of evaluating their development to attain maximum productivity. Nashville neurofeedback therapy is an amazing choice of such treatments.
For example, the person may attempt to enhance neural processes depending on alterations in the audio or film. The majority of neurofeedback therapy methods concentrate on Treatments for an alpha, beta, delta, theta, and gamma, as well as combinations of these, including alpha/theta proportion, beta/theta ratio, and so on. Nevertheless, alpha, beta, theta, and alpha/theta ratio are the most widely utilized procedures. They covered many professional and scientific features of distinct neurofeedback therapy procedures in this research.
Distinct Rate Elements of Neurofeedback Therapy:
Brain cell movements include a wealth of data regarding neurogenesis. Electromagnetic spikes produce synapses during stimulation. The activity of the mind, known as EEG, may be measured by putting electrodes on the skull. EEG creates a form of synchronized neurotransmission known as pyramidal cells, and the power produced is mirrored in the body layer where the items are. The magnitude and rhythms of various neuronal impulses, called cerebral oscillations, might be distinguished. The frequency of oscillations every minute (Hz) shows how rapidly the pulses fluctuate, and the magnitude denotes the strength of such oscillations, expressed in microvolts (V).
Delta (or less 4 Hz), θ (4–8 Hz), alpha (8–13 Hz), beta (13–30 Hz), and gamma (30–100 Hz) are the distinct harmonic parts that each indicates a diverse biological activity. In overview, vibrations appear in the EEG transmitter whenever an individual is sleeping, brainwaves appear when an individual is tired, and alpha ripples appear when an individual gets back. Their musculature is soft, but they are fully conscious; beta waves appear whenever an individual is awake, and ionization ripples appear when a patient is fully conscious.
Neurofeedback Therapy Threats:
Neurofeedback therapy is a security procedure with little danger. One research’s main prevalent negative symptoms were headphone irritation and sleepiness, albeit sleepiness was considered a favorite. Secondary impact by attendees with severe suffering, concussion, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) enabled them to rest. However, treatment investigations in individuals with melancholy and CNS damage suggested that restlessness, memory deficits, anxiousness, impatience, and hostility might have adverse consequences. With the possibility of adverse benefits, there was a chance that neurofeedback therapy would not work for anyone with the possibility of adverse benefits and that its impacts didn’t stay, resulting in a waste of taxpayer cash. There is still the possibility of being harmed.
Types of Neurofeedback Therapy:
For the management of diverse illnesses, there are seven forms of neurofeedback:
1. Frequency/power neurofeedback is the more often employed type of neurofeedback. Contact neurofeedback is a method that uses 2 to 4 electrical stimulation. It “interfaces neurofeedback.” It manages ADHD, stress and sleeplessness by altering the magnitude or frequency of specific neural activity in individual cerebral areas.
2. Slow cortex current neurofeedback (SCP-NF) helps people with ADHD, seizures, and headaches by improving the orientation of their slow brain possibilities.
3. A reduced neurofeedback system (LENS) sends a faint electric surge to the nervous system when immobile individuals and their eyelids shut. Every neurofeedback has TBI, ADHD, sleeplessness, arthritis, troubled leg disease, stress, melancholy, and rage.
4. Hem encephalographic (HEG) neurofeedback alleviates migraines by providing information on perfusion.
5. Z-score in real-time Sleep treats neurofeedback. It presents a mechanism for comparing parameters of brain waves to a database to ensure necessary input.
6. Electrical interference neuroimaging (LORE-TA) includes monitoring phases, amplitude, and synchronization using 19 sensors. Vices, anxiety, and compulsive disease are all treated using neurofeedback.
7. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is the most modern kind of neurofeedback that uses active input from deeper thalamic parts of the brain to control brain function.
ADHD, stress, melancholy, seizures, autism developmental disease, sleeplessness, and other illnesses. Specialists caution that because medical evidence is unclear, it is adequate to supplement more proven therapies and drugs. Devices within those gadgets scan the brain patterns and offer data about neural activity. Physicians treat them for individuals who do not have a particular diagnosis, particularly during difficult periods, because they may aid with stress and mood management. One advantage of neurofeedback therapy is that it is a narcotic. Which will never produce the negative consequences that several drugs entail.
Inference:
Honestly, one will never notice benefits when one leaves the workplace. According to a national public health care company, neurofeedback therapy may require six to twenty treatments. At the same time, there is no specific quantity of treatments that assures long-term outcomes and the length of treatment. Which will differ depending on the individual. A discussion with the providers about the number of visits required is necessary. The clinician must monitor progress by following complaints and measuring responsiveness at the start and conclusion of every treatment and what the client is doing during appointments.




